measuring endometrial thickness with fluid|normal endometrial thickness guidelines : makers Transvaginal ultrasonography is appropriate for an initial evaluation of postmenopausal bleeding if the ultrasound images reveal a thin endometrial echo (less than or equal to 4 mm), given that . How do I enable 2FA? Go to the ACCOUNT page. Click the PASSWORD & SECURITY tab. Under the 'TWO-FACTOR AUTHENTICATION' header, you will see the available 2FA .
{plog:ftitle_list}
16 de nov. de 2023 · Veja as dezenas sorteadas e o prêmio de R$ 1,7 milhão da Lotofácil 2955, realizada em 16 de novembro de 2023. Saiba como apostar, quanto custa e como .
normal range for endometrial thickness
Endometrial thickness is well assessed on MRI. Measurement should be taken at a mid-sagittal slice, similar to the ultrasound assessment plane. T2: normal endometrium is .
Transvaginal ultrasonography is appropriate for an initial evaluation of postmenopausal bleeding if the ultrasound images reveal a thin endometrial echo (less than or equal to 4 mm), given that .
Quantitative assessment of endometrial thickness, intrauterine lesions and intracavitary fluid. The endometrial thickness is the maximum measurement in the sagittal .The measurement of the total double-layer thickness should be reported in millimeters, rounded up to one decimal point. When intracavitary fluid is present, the thickness of both single .
Normal range of endometrial thickness. The designation of normal limits of endometrial thickness rests on determining at which thickness the risk of endometrial carcinoma is .Abstract: Measurement of endometrial thickness with ultra sonography is a modality commonly used today. Its clinical importance and applications extend throughout the phases . Fluid in the endometrial cavity and the hypoechoic subendometrial zone are not included in the measurement. Underlying uterine pathology such as adenomyosis and leiomyoma can make evaluation of the . Fluid in the endometrial canal can be a result of various underlying causes. Understanding these causes is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment: Menstrual Cycle: One common cause of fluid in the endometrial canal is related to the menstrual cycle. During menstruation, the endometrial canal can accumulate fluid and tissue that is expelled .
normal endometrial thickness ultrasound
Endometrial thickness varies according to a woman's age and menstrual cycle. A healthy endometrium is essential for a healthy pregnancy. An endometrial thickness of less than 14 mm is typically considered normal at any stage of the menstrual cycle. During menstruation, the endometrial thickness of pre-menopausal women ranges between two and . Endometrial Stripe, Sagittal View of the Uterus on Ultrasound). Occasionally, a small amount of anechoic fluid is noted in the endometrial canal in postmenopausal women. In such cases, the endometrial thickness is . Endometrial thickness throws light at not only the condition of the uterus, the favorability for conception and the health of the pregnancy, but it also shows hormonal changes, points to other disease conditions and is an important indicator in various assessments of a woman’s reproductive health.
6. How is endometrial thickness measured? Since the endometrium is a female reproductive organ, the most efficient and common way to measure an endometrium is by using an ultrasound. Not only does it measure the thickness, but it also checks the health of the uterine lining and the associated organs in the vicinity. The endometrium demonstrates a wide spectrum of normal and pathologic appearances throughout menarche as well as during the prepubertal and postmenopausal years and the first trimester of pregnancy. Disease entities include hydrocolpos, hydrometrocolpos, and ovarian cysts in pediatric patients; gestational trophoblastic disease during pregnancy; .Endometrial fluid | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org
Endometrial thickness before and after period Endometrium in the proliferative phase: 5-11 mm. After menstruation , the endometrium enters the so-called proliferative phase (which corresponds to the follicular phase of the cycle). During this stage, the mucous membrane thickens and is enriched with blood vessels under the action of estrogen , starting to prepare .
The uterine lining is called the endometrium. During an imaging test, it’ll show up as a dark line. This is the “endometrial stripe.” Here’s how this tissue can change with age, symptoms .Proportion of the myoma protruding into the uterine cavity: (a) grade 0 (100% in the cavity); (b) grade 1 (3 50% in the cavity); (c) grade 2 (< 50% in the cavity).With permission from: 17 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2010; 35: 103–12. The technique of FIS is easy, simple and well tolerated by the patients. 18 An open sided speculum is inserted to visualise the cervix, the . Proper care should be taken to not include hypoechoic myometrium or intrauterine fluid in this measurement. Measurement of Endometrium Thickness Range. . However, an endometrial thickness measurement of 7 mm after menopause may not necessarily indicate a significant health concern on its own. The thickness of the endometrium can be affected .
pleted using the search terms "endometrial thickness," "endometrium," and "ultrasound." Studies that were included in the review were those that correlated ultrasound measure ments of endometrial thickness with endometrial histology, or examined the effects of hormone replacement therapy (HRT), tamoxifen, and raloxifene on endometrial .Premenopausal Normal Findings. Ultrasound can accurately determine the endometrial stage of the menstrual cycle. 2 During the menstrual phase, the endometrium appears as a thin, echogenic line, measuring less than 4 mm (Fig. 4 demonstrates this from a different etiology). The echogenicity is secondary to acoustic reflections at the interface of the 2 sides of the .
Endometrial hyperplasia is when the lining of your uterus (endometrium) becomes too thick. Your endometrium is the lining that you shed during your menstrual period. It’s also the tissue that a fetus grows into during pregnancy. In some women and people assigned female at birth .Quantitative assessment of endometrial thickness: (Figures 4-7) The endometrial thickness is the maximum measurement in the sagittal plane and includes both endometrial layers (double endometrial thickness). It is critical to ensure that the uterus is in a midsagittal plane, the whole endometrial stripe is seen from the fundus to the endocervix .
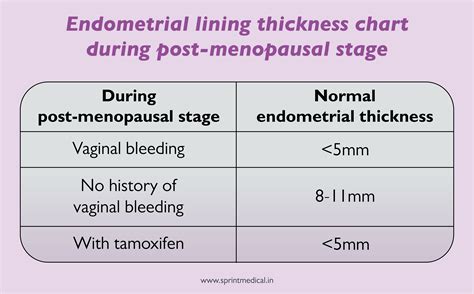
o the acceptable range of endometrial thickness is less well established in this group, cut -off values of 8 11 mm have been suggested ref required o the risk of carcinoma is ~7% if the endometrium is >11 mm, and 0.002% if the endometrium is <11 mm 8
normal endometrial thickness in premenopausal
Abstract. Objective: In clinical settings, transvaginal ultrasound has been used to evaluate abnormal vaginal bleeding. Because the endometrium responds to estrogens, endometrial thickness may constitute a biomarker of .Fig. 1. Pitfalls in evaluating the endometrium. A Incorrect measurement of the endometrium. The sonographer mea-sured the median echogenic layer (arrow) of the trilaminar endometrium, underestimating the thickness. B Incorrect measurement of the endometrium. Echogenic fluid (arrow)is present within the endometrial cavity and was included in theCT image through the uterus shows fluid-filled cavity marginated by tumor involving most of the endometrial surface and the endocervical region. An enlarged lymph node is evident at the right pelvic sidewall. . and the timing of the measurement of endometrial thickness is not critical. Normal post-partum endometrium. (a) Post-partum second week – fluid, debris and minimal gas shadows seen in the endometrial cavity. Single-layer thickness of the endometrium was 4.4 mm. (b, c) Uterus – on post-partum Day 18 with (b) single-layer endometrial thickness of 3.5 mm.
– Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): An infection of the female reproductive organs, including the uterus, can lead to fluid buildup. – Endometrial cancer: In rare cases, uterine cancer can cause fluid accumulation in the uterus. Symptoms of Fluid in the Uterus. The symptoms of fluid in the uterus can vary depending on the underlying cause . Thickened endometrium with internal fluid or gas suggests endometritis. It may be associated with other pelvic inflammatory signs like parametrial inflammation, fluid collection in the pouch of Douglas, and/or pyosalpinx. . Endometrial hyperplasia: It is diagnosed by measuring combined endometrial thickness. There may be focal or diffuse .The presence of endometrial fluid detected by transvaginal ultrasonography is a good marker for pathological changes of the endometrium in postmenopausal women if the endometrial thickness is greater than 4 mm. If the endometrial thickness is 4 mm or less, the presence of endometrial fluid is not an . The endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus. Its thickness varies with a woman’s age, reproductive stage and specific point of her menstrual cycle. A thickened endometrium may or may not be a normal finding, depending on various factors of a woman’s menstrual stage.
secretory phase (day 16 to 28): thickened hyperechoic endometrium measuring up to 16 mm; Postmenopausal women: regular, thin hyperechoic line measuring up to 5 mm, representing the remaining basal layer of endometrium; Please see the separate article on endometrial thickness for a detailed discussion of measurements and pathological .
Endometrial polyp depicted by saline infusion sonohysterography. A: Sagittal midline transvaginal view of the uterus demonstrates focal homogeneous thickening of the endometrium (calipers), measuring 16.6 mm in thickness, at the fundus. B: After instillation of saline, a polyp (arrow) is seen projecting into the fluid (S) in the uterine cavity. The correct endometrial measurement is obtained by subtracting the thickness of the fluid from the overall endometrial thickness—in this case (0.72 cm − 0.27 cm = 0.45 cm). B, Postmenopausal endometrium with fluid. Sagittal ultrasound shows a normal thin, echogenic endometrium separated by fluid.
normal endometrial thickness guidelines
volumetric karl fischer titration astm distributors
webWe would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
measuring endometrial thickness with fluid|normal endometrial thickness guidelines